France Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By End-Users, By Type of Temperature, By Ownership Model, By Mode of Transport, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0272
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “France Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By End-Users, By Type of Temperature, By Ownership Model, By Mode of Transport, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics industry in France. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the France Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by service segment, temperature range, region, cause and effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and challenges.
France Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The France cold chain market reached a valuation of EUR 8.7 Billion in 2023, driven by the increasing demand for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, growth in e-commerce grocery deliveries, and expansion of food exports including dairy, seafood, and frozen processed foods. Major players such as STEF, Kuehne + Nagel, DB Schenker, Chronofresh, and GEFCO are active in the French market, offering extensive temperature-controlled storage and transportation solutions across the country and Europe.
In 2023, STEF expanded its frozen warehouse capacity in Lyon to address the rising demand for frozen food storage, particularly from retail and HoReCa sectors. Paris, Lyon, Marseille, and Lille have emerged as key logistics hubs due to their proximity to food production zones and dense urban consumption centers.
%2C%202019%E2%80%932024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of France Cold Chain Market:
Boom in Pharmaceutical & Vaccine Logistics: The pandemic and the subsequent focus on vaccine storage and distribution catalyzed cold chain investments. In 2023, pharmaceutical logistics accounted for nearly 30% of total cold chain demand in France. The rollout of mRNA vaccines and other biologics that require ultra-low temperatures has further strengthened this trend.
Surge in Online Grocery & Fresh Delivery Services: Online grocery delivery in France grew by over 20% YoY in 2023, led by platforms such as Carrefour, Monoprix, and Amazon Fresh. With consumers increasingly expecting same-day or next-day delivery of chilled and frozen foods, cold chain providers are partnering with retailers to establish micro-fulfillment centers and refrigerated last-mile delivery networks.
Export of Agri-Food Products: France is one of the largest exporters of cheese, wine, meat, and seafood in Europe. To maintain compliance with EU and international food safety standards, exporters have scaled up investments in cold storage and reefer transportation. In 2023, over 60% of high-value perishable exports utilized integrated cold chain services.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of France Cold Chain Market
High Operational Costs and Energy Prices: Operating cold storage and refrigerated transportation networks in France remains highly cost-intensive due to surging energy prices, especially in the wake of the European energy crisis. In 2023, cold chain operators witnessed an average 12–15% increase in electricity costs, directly impacting profit margins. This challenge disproportionately affects small and mid-sized players with limited energy efficiency investments.
Infrastructure Gaps in Semi-Urban and Rural Areas: Despite robust infrastructure in urban and industrial clusters, France still faces cold chain coverage gaps in peri-urban and rural regions. Nearly 28% of agri-food producers in eastern and southwestern France reported delays or spoilage due to limited access to refrigerated logistics. This restricts their ability to reach high-value urban markets, especially for short shelf-life items like berries, artisanal cheese, and seafood.
Stringent Environmental and Refrigerant Compliance: New EU mandates under F-Gas Regulation (EU 517/2014) are phasing down hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), compelling cold storage operators to shift to low-GWP refrigerants. However, retrofitting existing equipment can cost anywhere between EUR 100,000 to EUR 500,000 per facility, acting as a major deterrent, particularly for facilities built before 2010.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Which Have Governed the Market
ATP (Accord Transport Perissable) Compliance: France mandates adherence to ATP rules for all cross-border transportation of perishable food products. As of 2023, over 85% of refrigerated transport fleets were ATP-certified, with remaining players being pushed to upgrade by 2026 under EU oversight. These certifications are vital for exports and long-haul food logistics within Europe.
French Anti-Waste Law (AGEC 2020): The Anti-Waste for a Circular Economy Act mandates reduced food loss, traceability of temperature-sensitive products, and better cold chain accountability. Large food retailers are required to donate unsold perishables rather than discard them, which necessitates real-time temperature monitoring during redistribution—stimulating demand for IoT-enabled cold logistics.
Incentives for Green Cold Chain Infrastructure: The French government, under the France 2030 investment plan, offers subsidies for cold chain operators investing in solar-powered refrigeration units, green refrigerants, and smart tracking systems. In 2023, over EUR 120 million was allocated to modernize cold chain logistics, primarily targeting SME service providers and food cooperatives.
France Cold Chain Market Segmentation
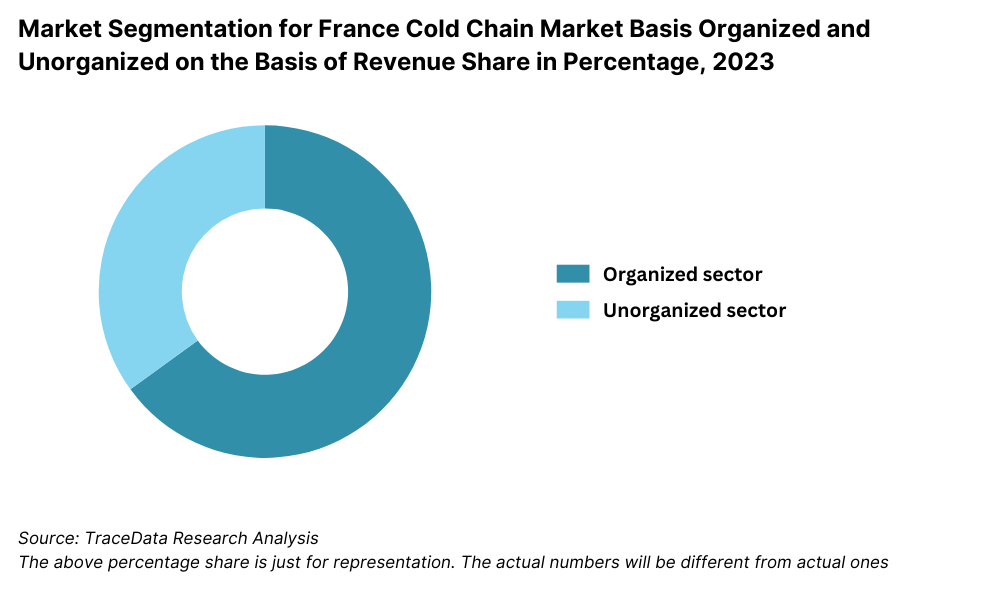
By Market Structure: Organized players dominate the cold chain market in France due to their advanced infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and integration with major retail and pharmaceutical supply chains. Companies like STEF, DB Schenker, and Kuehne + Nagel offer end-to-end solutions, including cold storage, refrigerated transport, and real-time temperature tracking. Unorganized players still hold relevance in rural areas and for small-scale distributors due to lower pricing and flexible delivery models, but they face challenges with technology upgrades and meeting EU compliance standards.
By End-User Industry: The food and beverage sector holds the largest share of the cold chain market, driven by France’s strong dairy, meat, and frozen food production. Supermarkets, hypermarkets, and quick-commerce grocery platforms have increasingly partnered with cold chain providers to ensure freshness and compliance. The pharmaceutical sector is the second largest, driven by stringent temperature requirements for vaccines, biologics, and specialty medicines. With growing exports of these sensitive products, pharma logistics are expected to witness accelerated investment.
.png)
By Type of Temperature: Chilled storage (2°C to 8°C) leads the market due to its application in dairy, fruits, vegetables, and certain pharmaceuticals. Frozen storage (below -18°C) follows, supported by rising frozen food consumption and export. Ultra-low temperature logistics (below -40°C), though niche, are gaining traction due to the storage requirements of mRNA vaccines and cell/gene therapies.
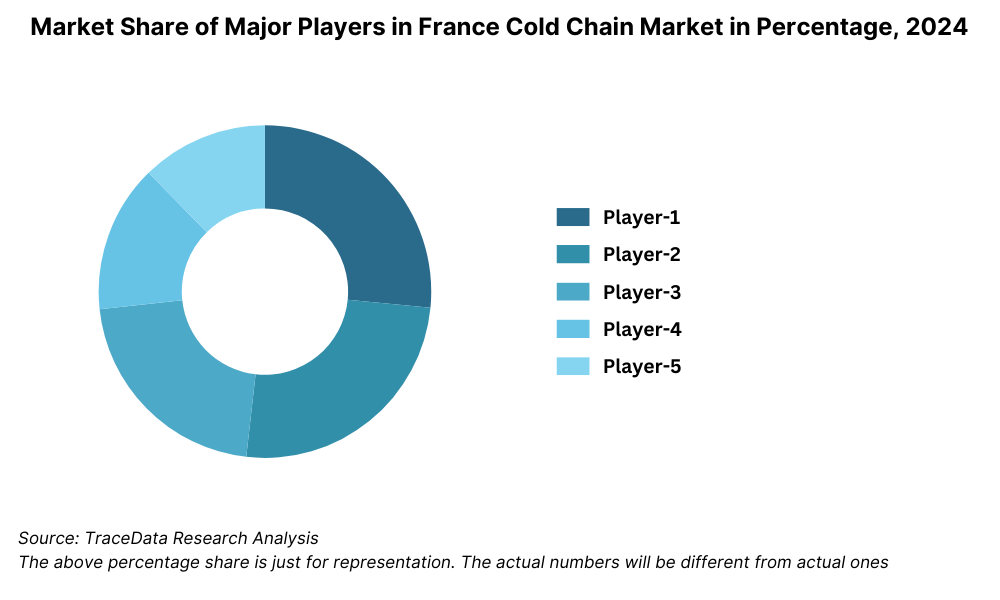
Competitive Landscape in France Cold Chain Market
The France cold chain market is moderately concentrated, with a few large players holding significant market share, particularly in the organized segment. However, the market is also witnessing the emergence of niche service providers and digital logistics startups offering specialized temperature-controlled solutions. Key players include STEF, Kuehne + Nagel, DB Schenker, Chronofresh, GEFCO, and Sofrilog, each known for their cold storage, refrigerated transport, and last-mile temperature-sensitive delivery services.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
STEF | 1920 | Paris, France |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany |
Chronofresh | 2015 | Paris, France |
GEFCO | 1949 | Puteaux, France |
Sofrilog | 2007 | Caen, France |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
STEF: As France’s largest cold chain logistics provider, STEF operates over 240 temperature-controlled sites across Europe. In 2023, the company expanded its frozen storage capacity in Lyon and Bordeaux, increasing its total cold storage footprint by 8%. STEF also reported a 6% YoY revenue growth, driven by growing demand from the retail and HoReCa segments.
Kuehne + Nagel: A global logistics player with a strong presence in France, Kuehne + Nagel reported increasing demand for pharmaceutical cold chain solutions. In 2023, they launched a new GDP-certified pharma hub near Charles de Gaulle Airport to support global vaccine and biologic shipments. The firm also invested in real-time monitoring technology for high-value medical logistics.
DB Schenker: Known for its comprehensive supply chain solutions, DB Schenker has been focusing on green cold chain logistics. In 2023, they launched a pilot project using electric refrigerated trucks in urban areas such as Paris and Marseille. The company also signed new contracts with leading French dairy producers for temperature-controlled exports.
Chronofresh: A subsidiary of Chronopost, Chronofresh specializes in temperature-controlled last-mile delivery. In 2023, it expanded its same-day delivery services to 25 new cities in France, addressing rising demand for fresh grocery and meal-kit deliveries. The platform handled over 12 million parcels in chilled and frozen categories.
GEFCO: Initially focused on automotive logistics, GEFCO has diversified into cold chain solutions for food and pharma. The company reported a 20% increase in cold chain-related contracts in 2023, largely due to its value-added services such as customs clearance and multimodal temperature tracking.
Sofrilog: A joint venture between transport company Sofrica and logistics provider Logistique Alimentaire, Sofrilog has a strong footprint in coastal and export-oriented regions. In 2023, it invested EUR 25 million to expand its cold storage capacity near Le Havre port, focusing on seafood exports and imported frozen goods.
What Lies Ahead for France Cold Chain Market?
The France cold chain market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a healthy CAGR during the forecast period. This growth will be driven by the rising need for temperature-controlled logistics in pharmaceuticals, increased consumption of frozen and convenience foods, and strong regulatory compliance across the food and healthcare sectors.
Expansion of Biopharma and Vaccine Logistics: As France continues to be a key hub for pharmaceutical manufacturing and R&D in Europe, demand for ultra-cold and highly specialized temperature-controlled logistics is expected to rise. Growth in biologics, cell & gene therapies, and vaccine exports will drive investment in dedicated pharma-grade cold storage and GDP-compliant transport networks.
Digital Transformation in Cold Chain Monitoring: The adoption of real-time temperature tracking, IoT-enabled sensors, and blockchain-based traceability systems is expected to accelerate. These technologies will enhance visibility, reduce spoilage rates, and improve regulatory compliance—particularly for export shipments requiring stringent temperature documentation.
Increased Demand for Frozen & Processed Foods: Changing consumer lifestyles and the popularity of ready-to-eat and frozen food products are expected to significantly boost the frozen cold chain segment. Urbanization and the growth of quick commerce platforms are also expected to drive higher demand for frozen storage and last-mile refrigerated delivery.
Sustainability and Green Cold Chain Initiatives: France’s environmental agenda and EU carbon neutrality goals will shape the future of cold chain infrastructure. Companies are increasingly investing in solar-powered warehouses, low-GWP refrigerants, and electric refrigerated vehicles. These green logistics solutions are expected to become a core differentiator in the coming years.
%2C%202024%E2%80%932030_YCBPtxc.png)
France Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Captive Cold Chain Infrastructure
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
• By End-User Industry:
o Food & Beverage
o Dairy and Frozen Products
o Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines
o Horticulture & Floriculture
o Seafood & Meat
o Quick Commerce & Grocery Delivery
• By Type of Temperature:
o Chilled (2°C to 8°C)
o Frozen (Below -18°C)
o Deep-Frozen/Ultra-Cold (Below -40°C)
• By Ownership Model:
o Private Warehousing
o Public Warehousing
o Contract Logistics
o Cooperative Cold Storage
• By Mode of Transport:
o Road Transport
o Rail Transport
o Air Cargo
o Sea Freight (Reefer Containers)
• By Region:
o Île-de-France (Paris and surrounding region)
o Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
o Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
o Nouvelle-Aquitaine
o Hauts-de-France
o Grand Est
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• STEF
• Kuehne + Nagel
• DB Schenker
• Chronofresh
• GEFCO
• Sofrilog
• FM Logistic
• TSE Express Médical
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Storage & Logistics Companies
• Pharmaceutical & Food Exporters
• E-Grocery & Retail Distribution Firms
• Supply Chain & IoT Technology Providers
• Regulatory Bodies (e.g., French Ministry of Agriculture, EU Commission)
• Infrastructure Investment Firms
• Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for France Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for France Cold Chain Market
4.4. Demand Decision-Making Process
4.5. Supply Decision-Making Process
5.1. Cold Chain Infrastructure Landscape in France, 2018-2024
5.2. Chilled vs. Frozen Capacity Comparison, 2018-2024
5.3. Share of Organized vs. Unorganized Players, 2023-2024
5.4. Cold Chain Utilization Rate by End-Use Sector, 2023-2024
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Cold Storage Capacity and Volume Moved, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By End-User (Food, Dairy, Pharma, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Temperature (Chilled, Frozen, Deep-Frozen), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Ownership Model (3PL, Captive, Public, Private), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (ÃŽle-de-France, Nouvelle-Aquitaine, etc.), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Logistics Integration Decisions
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for France Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for France Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for France Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for France Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations for France Cold Chain Market
12.1. Market Size and Growth of Quick Commerce and Cold Chain in Pharma, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Cold Chain Players: Infrastructure, Clients, Reach, Revenue Mix, and Innovations
13.1. Infrastructure Financing and Investment Trends, 2018-2029
13.2. Public-Private Partnerships and Government Incentives
13.3. Role of EU Green Investment and France 2030 Plan
13.4. Cold Chain Financing Split by Banks, Government Agencies, and Institutional Funds
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors Including Company Overview, Infrastructure, Technology Adoption, Service Portfolio, Cold Storage Capacity, Delivery Reach, and Value-Added Services
16.2. Strength and Weakness Analysis
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Cold Chain Volume Moved and Storage Capacity, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.3. By Type of Temperature, 2025-2029
18.4. By Ownership Model, 2025-2029
18.5. By Mode of Transport, 2025-2029
18.6. By Region, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the France Cold Chain Market. This includes cold storage operators, refrigerated transport providers, temperature-controlled packaging companies, pharma and food exporters, grocery retailers, and last-mile logistics providers.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, cold chain-specific journals, public and proprietary databases such as Eurostat, INSEE, Business France, and market intelligence platforms to perform desk research and collate market-wide information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the cold chain market, aggregating insights on market size, regional distribution, pricing trends, export and import dynamics, and segment-specific developments (e.g., frozen vs. chilled logistics).
We supplement this research with company-level investigations through press releases, annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. These documents help assess the financial performance, infrastructure investments, client contracts, and technology adoption of key players.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives, supply chain managers, cold storage operators, refrigerated transporters, and retail distribution heads across France. These interviews aim to validate market assumptions, verify statistical data, and gather key insights on operational capacity, technology integration, pricing, challenges, and future outlook.
As part of our validation strategy, our team conducts disguised interviews by approaching companies as potential clients. This approach enables cross-verification of information provided by company representatives, including revenue streams, infrastructure scale, service pricing, and typical client SLAs.
• Bottom-up analysis is undertaken to estimate volume handled per player, aggregated to arrive at the total market size.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A combination of bottom-up and top-down approaches, supported by triangulation methods, is applied to validate the market sizing and segmentation estimates. Internal benchmarks and modeling tools are used to ensure logical consistency and industry alignment across all findings.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the France Cold Chain Market?
The France cold chain market is poised for steady and sustained growth, projected to surpass EUR 12 Billion by 2029. This growth is supported by rising demand for temperature-sensitive logistics in pharmaceuticals, increased consumption of frozen and convenience food, and stringent EU food safety and pharmaceutical compliance regulations. France’s strategic role as a leading agri-food and pharmaceutical exporter further enhances the market's long-term potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the France Cold Chain Market?
The France Cold Chain Market includes several prominent players such as STEF, Kuehne + Nagel, DB Schenker, Chronofresh, and GEFCO. These companies dominate the organized sector with their nationwide cold storage infrastructure, GDP-compliant pharma logistics, and reefer transport fleets. Other notable players include Sofrilog, FM Logistic, and TSE Express Médical.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the France Cold Chain Market?
Key growth drivers include the expansion of biologics and vaccine supply chains, growing e-commerce demand for fresh and frozen food delivery, and investments in sustainable cold chain infrastructure. Regulatory compliance, such as ATP and EU F-Gas regulations, is also pushing operators to modernize facilities and adopt real-time monitoring technologies—further stimulating growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the France Cold Chain Market?
The market faces several challenges including high energy and operational costs, gaps in cold chain infrastructure across rural and semi-urban regions, and significant capital required for upgrading to low-GWP refrigerants. Adherence to evolving EU regulations and ensuring temperature compliance across long-haul logistics also pose operational challenges for both large and small players.