Indonesia Agritech Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Technology, By Application, By Consumer Demographics, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0012
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2024
- Total Pages: 80-100
Report Summary
The report titled "Indonesia Agritech Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Technology, By Application, By Consumer Demographics, and By Region" provides a comprehensive analysis of the agritech sector in Indonesia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, consumer profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Agritech Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on market growth, technological advancements, region, cause and effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Indonesia Agritech Market Overview and Size
The Indonesia agritech market reached a valuation of USD 10 billion in 2023, driven by the increasing need for enhanced agricultural productivity, a growing population, and a focus on sustainable farming practices. The market is characterized by major players such as TaniHub, Crowde, Eragano, and HARA. These companies are recognized for their innovative technological solutions, extensive farmer networks, and customer-focused approaches aimed at improving agricultural outputs and efficiency.
In 2023, TaniHub launched a new AI-powered platform to enhance farmer productivity and streamline the agricultural process through real-time data analysis. This initiative aims to tap into Indonesia's growing digital economy and provide a more efficient and profitable farming experience. Key regions such as West Java and Central Java are critical markets due to their high agricultural activity and digital adoption rates.
Market Size for Indonesia Agritech Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2018-2024

Source: TraceData Research Analysis
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Indonesia Agritech Market:
Technological Innovation: The introduction of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain has significantly enhanced agricultural productivity and efficiency in Indonesia. In 2023, agritech solutions contributed to a 15% increase in crop yields, as more farmers adopted precision farming techniques. This trend is particularly pronounced among smallholder farmers seeking to optimize resources and reduce costs.
Government Support: The Indonesian government’s push for digital transformation in agriculture has been a key driver of growth. Initiatives such as Smart Farming Indonesia and financial support for agritech startups have enabled the adoption of innovative farming practices. In 2023, government-backed agritech programs benefited around 30% of Indonesia’s farming population, improving access to modern agricultural tools and techniques.
Rising Demand for Sustainable Farming: Growing awareness around sustainability and the need for food security has led to increased investment in agritech. Consumers and producers alike are focusing on environmentally friendly and sustainable practices. In 2023, approximately 25% of agritech startups in Indonesia were focused on sustainability, helping to drive growth in eco-friendly farming practices.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Indonesia Agritech Market
Infrastructure Gaps: Limited access to high-speed internet and reliable digital infrastructure remains a significant challenge, particularly in rural areas where agritech solutions are most needed. According to a recent industry survey, around 40% of farmers have reported difficulties in accessing the necessary digital tools to implement agritech solutions effectively, hampering adoption rates.
High Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for adopting advanced agritech technologies is prohibitive for many smallholder farmers. In 2023, it was estimated that approximately 35% of farmers hesitated to adopt these technologies due to the high costs associated with purchasing and maintaining new equipment, preventing widespread adoption across the agricultural sector.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The absence of clear guidelines and inconsistent regulations around the use of certain technologies, such as drones and blockchain for agriculture, has created barriers for agritech companies. In 2023, regulatory constraints affected around 25% of agritech firms, delaying the rollout of new technologies and limiting their ability to scale operations.
Lack of Skilled Labor: A shortage of skilled labor capable of operating advanced agritech tools and software is another barrier to growth. Approximately 30% of agritech firms in Indonesia reported difficulties in finding adequately trained personnel in 2023, slowing the deployment of cutting-edge technologies in the agricultural sector.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Digital Agriculture Regulations: The Indonesian government has implemented guidelines to regulate the use of digital tools in agriculture, including drone usage and data collection. These regulations focus on ensuring that agritech innovations adhere to safety, privacy, and ethical standards. In 2023, around 70% of agritech companies complied with these regulations, showcasing a positive trend toward standardized practices.
Agricultural Subsidies and Support: The government provides subsidies for farmers to adopt new technologies, such as automated irrigation systems, sensors, and AI-powered equipment. These subsidies have contributed to increased adoption of agritech tools, especially among small and medium-scale farmers. In 2023, approximately 40% of agritech-adopting farmers benefited from these financial support programs.
Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives: To promote environmentally sustainable farming practices, the Indonesian government has introduced incentives for agritech companies that focus on reducing carbon emissions and improving resource efficiency. This includes tax exemptions for firms engaged in sustainable practices. In 2023, around 15% of agritech companies took advantage of these incentives, reflecting growing governmental support for green agritech solutions.
Indonesia Agritech Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Agritech start-ups dominate the market due to their innovative approaches and strong focus on solving key agricultural challenges. These companies have built strong connections with local farmers and cooperatives, offering tailored solutions to meet specific agricultural needs. Government-backed agritech initiatives also hold a significant share, as they provide technical support and subsidies to encourage the adoption of advanced technologies. Established technology firms are gradually increasing their presence by leveraging their expertise in AI and IoT to develop scalable agritech solutions.
By Technology: AI-powered tools are the leading technology in the agritech market, offering predictive analytics, real-time crop monitoring, and optimized resource management. IoT-based sensors follow closely, with applications in precision farming, automated irrigation, and soil monitoring. These technologies have gained traction due to their ability to improve productivity and reduce costs for farmers.
By Application: Precision farming holds the largest share of the agritech market, offering solutions for optimizing crop yields, reducing waste, and improving the overall efficiency of farming operations. Supply chain management and farm management software are also gaining prominence, as they help streamline logistics and provide better oversight of farm activities.
Indonesia Agritech Market Segmentation
Farming as a Service (FaaS): The Farming as a Service (FaaS) vertical in Indonesia is the largest contributor to the Indonesia Agritech market. This market has seen a steady rise from FY’ 16 to FY’21. There has been a strong increase in demand for the services provided by FaaS startups in the last five years, which is mostly due to the increase in smartphone and internet penetration in Indonesia. The competition structure is monopolistic, with Sayurbox, Tanisupply, and Aruna leading the FaaS market.
Agri Fintech: Demand in the agri fintech sector is significantly driven by government support, which helps in achieving various goals related to financial inclusion and digital literacy, along with helping formalize one of the most informal economic sectors in the country. The competition structure is monopolistic, with Tanifund, eFishery, Koltiva and iGrow capturing the market share.
Market Access: The demand for upstream supply chain aggregators has not increased as much as other sub verticals such as FaaS, primarily due to greater levels of poverty among farmers and fishermen as compared to end consumers, most of whom reside in urban clusters in Indonesia. The competition structure is oligopolistic, with eFishery, Koltiva and 8villages making up almost all the market share by revenue.
AgriTech Driven: This vertical is the second largest contributor to the Agritech Industry of Indonesia in 2021, which covers the Agritech driven companies within sub-segments like hydroponics, aquaponics, vertical farming, dairy, poultry, meat, seafood. There are inherent demand limitations to mechanized farm products on small landholder farms due to the labour intensive nature of agriculture practiced by farmers, but there is a lot of scope for agritech products to significantly improve yields. The competition structure is oligopolistic, with Tanihub, Aruna, and Neurafarm leading the market on the basis of revenue generated.
Agri Biotech: Demand for Agri Biotech products is expected to grow exponentially as there is pressure on farming and fishing ecosystems throughout the world to produce more output to combat the problem of food security. The competition structure is oligopolistic, with Pandawa Agri and Magalarva making up almost the entire market share.
Competitive Landscape in Indonesia Agritech Market
The Indonesia agritech market is highly competitive, with a growing number of players bringing technological solutions to the agriculture sector. The market is evolving rapidly with the entry of new start-ups and the expansion of established companies like TaniHub, Crowde, Eragano, and HARA, offering farmers innovative solutions to improve productivity, transparency, and sustainability.
| Name | Founding Year | Headquarters |
| TaniHub | 2016 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| eFishery | 2013 | Bandung, West Java |
| Crowde | 2016 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| HARA | 2015 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Tanijoy | 2017 | Bandung, West Java |
| Koltiva | 2013 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Sayurbox | 2017 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| JALA | 2015 | Yogyakarta, Indonesia |
| iGrow | 2014 | Depok, West Java |
| Eragano | 2015 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
TaniHub: As one of the leading agritech platforms in Indonesia, TaniHub facilitated transactions worth over USD 100 million in 2023, marking a 30% increase compared to the previous year. The platform’s focus on connecting farmers with markets and providing supply chain financing has made it a key player in Indonesia’s agritech ecosystem.
Crowde: Specializing in agri-financing, Crowde supported over 200,000 farmers in 2023, seeing a 25% growth in user adoption. The company's emphasis on providing easy access to loans for smallholder farmers has helped bridge the financial gap in rural areas.
Eragano: Known for its end-to-end solutions, Eragano reported a 20% increase in its user base in 2023, driven by its comprehensive farm management tools that assist farmers in optimizing crop production and resource management.
HARA: Focused on data-driven agriculture, HARA collected valuable farm data from over 300,000 hectares of agricultural land in 2023. The platform’s efforts to increase transparency and efficiency in the supply chain have positioned it as a significant player in the Indonesian agritech market.
What Lies Ahead for Indonesia Agritech Market?
The Indonesia agritech market is projected to experience significant growth by 2029, exhibiting a robust CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is expected to be driven by advancements in technology, government support, and increasing focus on sustainability in agriculture.
Shift Towards Precision Agriculture: As the Indonesian government continues to invest in smart farming initiatives, there is anticipated to be a rise in the adoption of precision agriculture technologies. These technologies, supported by government incentives, will enable farmers to optimize resource use and increase crop yields, meeting the growing food demand.
Integration of AI and IoT: The integration of AI and IoT in farming practices is expected to revolutionize agriculture in Indonesia. These technologies will provide real-time data, enhance decision-making, and improve the efficiency of farming processes. The increasing use of AI-powered tools for crop monitoring and predictive analytics will streamline operations and boost productivity.
Growth of Agri-Financing Programs: With a growing number of agritech companies focusing on agri-financing, there will likely be increased access to credit for smallholder farmers. These programs will enable farmers to invest in technology and infrastructure, driving further growth in the agritech market.
Focus on Sustainable Farming Practices: There is a growing trend towards sustainability within the Indonesian agritech sector, with an emphasis on eco-friendly farming techniques, water conservation, and soil health management. These sustainable practices are expected to gain traction, supported by consumer demand for environmentally responsible agricultural products.
Expansion of Digital Marketplaces: The continued growth of digital agritech platforms will expand market access for farmers, providing them with better opportunities to sell their produce, access supply chain solutions, and receive valuable insights. The rise of these platforms is expected to drive further growth in Indonesia's agritech market, particularly in remote and underserved regions.
Future Outlook and Projections for Indonesia Agritech Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2024-2029
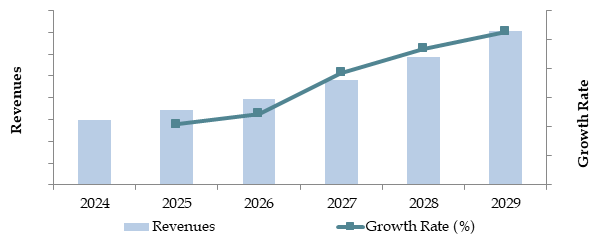
Source: TraceData Research Analysis

Indonesia Agritech Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
- Start-ups
- Government-backed Agritech Initiatives
- Established Technology Companies
- Organized Sector
- Unorganized Sector
- Commercial Agritech Solutions
- By Technology:
- AI & Machine Learning
- IoT Sensors
- Drones & Automation
- Blockchain for Supply Chain
- Robotics in Farming
- By Application:
- Precision Farming
- Supply Chain Management
- Farm Management Software
- Agri-Financing
- Sustainable Agriculture Solutions
- By Region:
- West Java
- Central Java
- Sumatra
- Sulawesi
- Eastern Indonesia
- By Farm Size:
- Smallholder Farms
- Medium-sized Farms
- Large Commercial Farms
- By Type of Crop:
- Rice
- Corn
- Palm Oil
- Coffee
- Horticulture
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- TaniHub
- eFishery
- Crowde
- HARA
- Tanijoy
- Koltiva
- Sayurbox
- JALA
- iGrow
- Eragano
Key Target Audience:
- Agritech Start-ups
- Government Agencies
- Agricultural Cooperatives
- Financial Institutions & Investors
- Technology Providers
- Research & Development Institutions
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Revenue Streams for Indonesia Agritech Market
4.2. Business Model Canvas for Indonesia Agritech MarkeT
5.1. Adoption of Agritech Solutions in Indonesia, 2018-2024
5.2. AgriTech vs Traditional Agriculture in Indonesia, 2018-2024
5.3. Spend on Agritech Solutions in Indonesia, 2024
5.4. Number of Agritech Companies and Startups in Indonesia by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024p
9.1. By Business Segment (FaaS, Fintech, Market Access, Agritech, Agri Biotech), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Location (Jakarta, Bogor, Bandung, Malang, Yogyakarta, Depok, Setiabudi, Tangerang, Bekasi, Sleman, Lampung, Arcamanik), 2023-2024P
10.1. Operating Model and Revenues Streams for FaaS Service Vertical
10.2. Timeline of Major Players in FaaS Service Vertical Segment
10.3. Service Portfolio of FaaS Players
10.4. Market Size for Indonesia FaaS Segment Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
10.5. Competition Scenario for Major Players in Indonesia FaaS Segment basis parameters including Funding, Funding Stage, Year of establishment, Location, Employee Size, Number of farmers served, No. of operational segments, Revenue, SWOT analysis and other parameters
10.6. Future Projections for FaaS Market in Indonesia Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
11.1. Operating Model and Revenues Streams for Fintech Service Vertical
11.2. Timeline of Major Players in Fintech Service Vertical Segment
11.3. Service Portfolio of Fintech Players
11.4. Market Size for Indonesia Fintech Segment Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
11.5. Competition Scenario for Major Players in Indonesia Fintech Segment basis parameters including Funding, Funding Stage, Year of establishment, Location, Employee Size, Number of farmers served, No. of operational segments, Revenue, Loans Financed, Amount Disbursed, NPA, SWOT analysis and other parameters
11.6. Future Projections for Fintech Market in Indonesia Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
12.1. Operating Model and Revenues Streams for Agritech Market Access Service Vertical
12.2. Timeline of Major Players in Agritech Market Access Vertical Segment
12.3. Service Portfolio of Agritech Market Access Players
12.4. Market Size for Indonesia Agritech Market Access Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
12.5. Competition Scenario for Major Players in Indonesia Agritech Market Access Segment basis parameters including Funding, Funding Stage, Year of establishment, Location, Employee Size, Number of farmers served, No. of operational segments, Revenue, Loans Financed, Amount Disbursed, NPA, SWOT analysis and other parameters
12.6. Future Projections for Agritech Market Access Market in Indonesia Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
13.1. Farmer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
13.2. Farmer Journey and Decision Making
13.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
13.4. Gap Analysis Framework
14.1. Trends and Developments for Indonesia Agritech Market
14.2. Growth Drivers for Indonesia Agritech Market
14.3. SWOT Analysis for Indonesia Agritech Market
14.4. Issues and Challenges for Indonesia Agritech Market
14.5. Government Regulations for Indonesia Agritech Market
17.2. Strength and Weakness
17.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
18.2. Adoption Rates, 2025-2029
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Indonesia Agritech Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 companies in the country, considering their financial data, technological offerings, and market reach.
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, secondary research, and proprietary databases to collect industry-level data for analysis.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is performed by referencing a wide array of secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables a thorough examination of the market, with a focus on factors like revenue streams, market players, technology adoption rates, and price levels. The data is further enriched by an analysis of company-level information sourced from press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and related documents. This method provides a foundational understanding of the agritech market and its key players.
Step 3: Primary Research
In-depth interviews are conducted with C-level executives, agritech start-ups, and end-users within the Indonesia Agritech Market. These interviews aim to validate market assumptions, authenticate statistical data, and gather valuable insights into the operational and financial dynamics of the market. A bottom-to-top approach is employed to assess the overall market by aggregating volume data from each player.
As part of the validation process, our team also executes disguised interviews by approaching companies as potential customers. This method allows us to verify the information shared by company executives, ensuring the data matches what is available through secondary sources. These discussions also provide a comprehensive view of revenue streams, value chains, and pricing mechanisms.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A top-to-bottom and bottom-up approach, combined with market size modeling exercises, is undertaken to ensure the accuracy of the data and to conduct a thorough sanity check.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Indonesia Agritech Market?
The Indonesia agritech market is expected to grow significantly, reaching a valuation of USD 500 million in 2023. This growth is driven by factors such as technological innovation, government support, and the increasing demand for sustainable agriculture solutions. The market’s potential is further amplified by the rise of digital platforms that enhance accessibility and efficiency in agriculture.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Indonesia Agritech Market?
The Indonesia Agritech Market includes prominent players such as TaniHub, Crowde, Eragano, and HARA. These companies dominate the market by offering innovative solutions, strong farmer networks, and a focus on improving productivity and sustainability. Other notable players include Tanifund and Eden Farm.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Indonesia Agritech Market?
The primary growth drivers include technological advancements, such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, which improve farming efficiency and crop yields. Government initiatives supporting smart farming and financial incentives for agritech adoption are also contributing to the sector’s expansion. Additionally, a growing focus on sustainability and food security is driving the demand for innovative agricultural solutions.
04 What are the Challenges in the Indonesia Agritech Market?
The Indonesia Agritech Market faces several challenges, including infrastructure gaps, particularly in rural areas, high initial costs for technology adoption, and a shortage of skilled labor. Regulatory uncertainties related to the use of new technologies also present barriers for market players.