Malaysia Logistics Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Mode of Transportation, By End-User Industry, By Region, and By Key Players
- Product Code: TDR0031
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2024
- Total Pages: 80-100
Report Summary
The report entitled "Malaysia Logistics Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Mode of Transportation, By End-User Industry, By Region, and By Key Players" provides a detailed analysis on the Malaysia Logistics Market. The report provides an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the logistics market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by mode of transportation, end-user industry, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Malaysia Logistics Market Overview and Size
The Malaysia logistics market had reached a valuation of MYR 45 Billion in 2023, moving on the wheels of strategic location, ever-growing trade activities, and rising e-commerce. The major players in this market include GD Express, Pos Malaysia, DHL Malaysia, and Tiong Nam Logistics, among others. These firms are well-known for their solid distribution networks, deployment of advanced technologies, and customer-oriented services.
In 2023, the company opened a new warehousing facility to meet the growing demand for cold chain logistics and expanded its services in the region. Kuala Lumpur and Penang are considered important markets due to high population density and good infrastructure.
Market Size for Malaysia Logistics and Warehousing Industry on the Basis of Revenue in USD Billion, 2018-2024
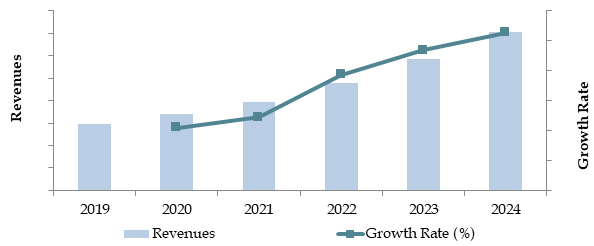
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Malaysia Logistics Market:
Strategic Location: It occupies a strategic location whereby its position on major shipping routes provides easy access for both exports and imports, therefore making it one of the region's most vital logistics hubs. Meanwhile, in 2023, about 60% of sea trade within Southeast Asia passes through Malaysian ports, thus stimulating further demand for quality logistics infrastructure and services.
E-commerce Boom: Growth within the field of e-commerce contributed much toward growth in this sector. The market size of Malaysian e-commerce showed an approximate 18% growth in comparison to the previous year of assessment, i.e., 2023, which contributed to a greater surge in the demand for logistics services at last-mile delivery levels, accounting as much as about 35% of entire revenues from logistical activities.
Government Investments in Infrastructure: The Malaysian government has been very instrumental in investing in the building of infrastructure that would support the operations of logistics. In 2023, the government proposed MYR 5 billion to be put toward the development of roads and the expansion of capacity at major ports. These investments have increased efficiency and furthered the capacity of the logistical networks, hence promoting market growth.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Malaysia Logistics Market
Bottlenecking Infrastructure: Though the investment in infrastructure has been continuous, a lot of inadequacies are still observable in the country's infrastructure. For example, in 2023, industry reports claimed that almost a quarter of all logistics companies were plagued by congestion in the ports and deficiencies in road connectivity, especially to rural areas, which delayed transit. This increases the cost of transportation and eventually affects the overall efficiency of logistics.
Regulatory Compliance: The high and complicated level of regulatory requirements throughout customs clearance procedures, together with the many safety standards being put in place, have often made life difficult for the logistics services of Malaysia. During 2019, 18% of the total shipments experienced delay in transit as the compliance rules prevailed at most border checkpoints. Such regulative factors obviously increase the total cost and decelerate the pace in the supply chain, thereby minimizing the market growth prospects of the companies pertaining to the delivery of services concerning logistics solutions in Malaysia.
Increasing Operational Costs: The cost of operation is increasing in Malaysia logistics industry due to rising fuel prices, labor costs, and technology investments. For instance, 30% of the logistics companies recorded a reduction in profit margins in 2023 largely due to a 12% increase in fuel prices. These are especially crippling to the small players in logistics, who have to struggle to be able to compete in the market.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Customs Clearance Regulations: The Malaysian government has imposed some serious customs clearance policies for systematic export and import, such as doing all documents electronically and including the specific necessities on the aspect of safety and security. Some regulations include that all the paperwork must be submitted electronically and specify rigorous safety and security requirements. In 2023, electronic customs clearances were able to be put into operation in the major ports to increase efficiencies by 85% of logistic firms, thus considerably shortening their time at each processing terminal.
National Transport Policy 2019-2030: This will ensure that Malaysia's transport and logistics sectors become efficient through the development of infrastructure, integration with technology, and environmental sustainability. The government, under this policy, allocated MYR 6 billion in 2023 for various infrastructural works that included expanding the rail network and modernizing the ports to achieve better facilitation of logistics.
Regulations regarding environmental impact: The government of Malaysia has created policies to ensure sustainability in logistics to reduce carbon emissions. It gives some form of incentives to companies operating logistic services to move to using electric trucks, among other green technologies. This is expected to go higher with more companies taking advantage of the subsidies given to the companies by the government, where it gave tax exemption to all-for instance, in 2023, electric vehicles comprised 15% of the fleet that involved logistics in Malaysia.
Cold Chain Standards: The concerned government has imposed high standards for cold chain logistics, mainly on pharmaceutical transportation and perishable goods transportation. Such regulations oblige the companies to maintain a certain level of temperature control and also periodic audits. In 2023, 70% of cold chain logistics service providers follow standards and policies that guarantee the safety and quality of goods during transportation.
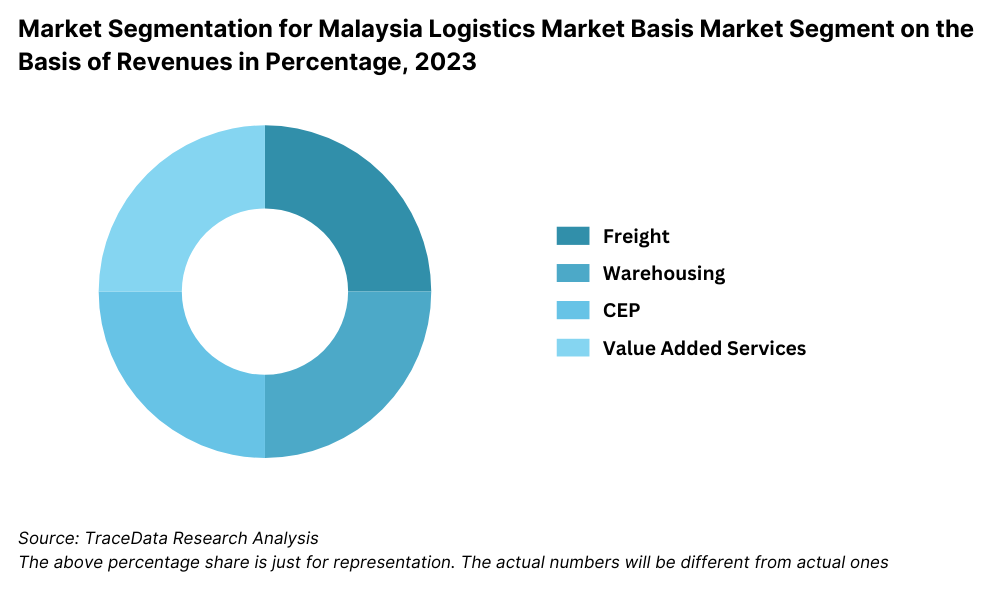
Malaysia Logistics Market Segmentation
Freight Forwarding: The growth of the freight forwarding market in Malaysia-international-much owes to the contribution of industries such as F&B, FMCG, and industrial. With continuous improvement in the road infrastructure, road freight is the most preferred mode of transportation, followed by air and sea freight. The well-developed road network in Malaysia provides an important connecting channel between the urban and rural regions, though transportation to some remote areas may still be somewhat difficult. The intra-Asia flow corridor dominated the freight forwarding industry of Malaysia in terms of revenue due to its strong trade tie-up within the region.
Warehousing: In Malaysia, warehousing has been on a gradually rising growth with increasing demand for modern and quality warehouses. While such growth is happening, the demand from ever-growing e-commerce and manufacturing still lags in state-of-the-art facilities. Secondly, warehousing is another area that requires much investment and advanced technologies in the development process of logistics. Automation and the addition of advanced inventory control systems will most likely give the warehousing market in Malaysia a huge boost by enabling better efficiency in operations and supply chain management.
CEP Market: CEP logistics in Malaysia have grown robustly at a CAGR during 2018-2023, driven by growing e-commerce activities. With the rapid growth of e-commerce in Malaysia, online shoppers increasingly ask for faster delivery options and more convenience in return processes. Though express delivery still remains a luxury service for many end-consumers, the rapid growth of e-commerce has intensified demand for quick and reliable logistics solutions. Future growth will also be supported by further expansion in e-commerce and increasing expectations of speedier services.
By End-User Industry: The retail and e-commerce industry is the largest end-user industry of logistics services in Malaysia, while the trend for online shopping and its efficiency in last-mile delivery continues to grow. Other major contributors are manufacturing and automotive industries that rely on strong logistics networks for transportation of raw materials and finished goods. The cold chain solution has been highly demanded from the segment of healthcare; at the same time, the oil & gas and agriculture sectors also continued to depend on logistics for the movement of bulk goods and machinery.
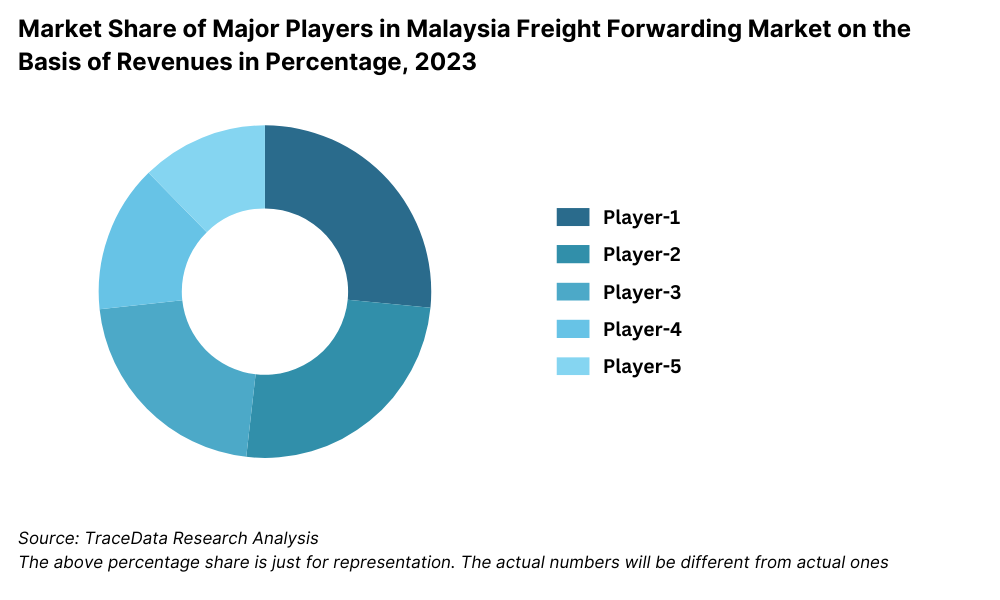
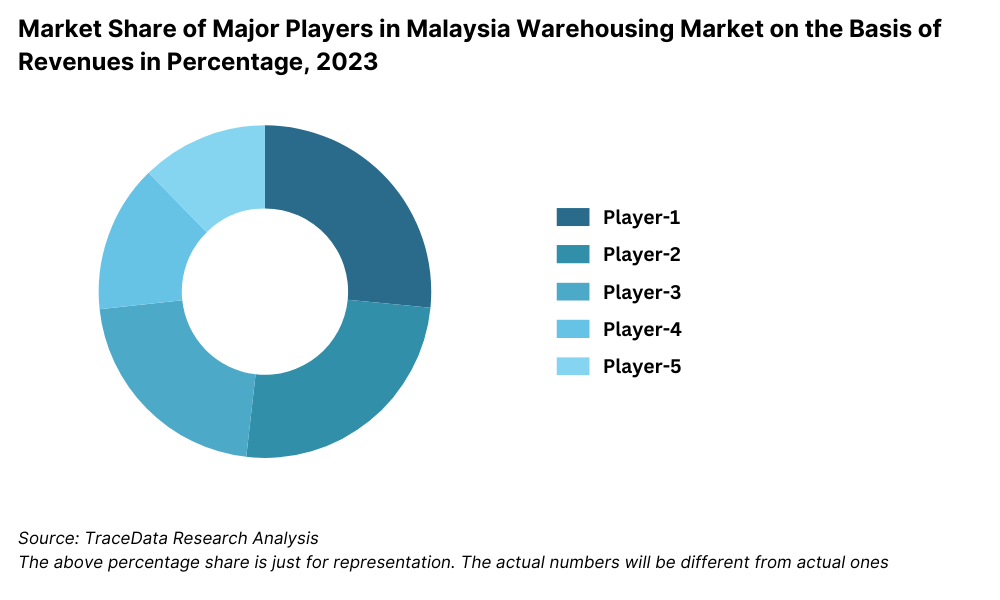
Competitive Landscape in Malaysia Logistics Market
The Malaysia logistics market is relatively concentrated, and has only a few leading players holding the major share. This landscape has varied with the advent of new entrants offering extensions in special types of logistics services such as e-fulfillment and cold chain, thus providing more options for companies with specialized services.
Company Name | Founding Year | Headquarters | Category |
Kerry Logistics | 1981 | Hong Kong | Freight Forwarding, Warehousing |
DHL Global Forwarding | 1969 | Bonn, Germany | Freight Forwarding |
Tiong Nam Logistics | 1975 | Johor Bahru, Malaysia | Freight Forwarding, Warehousing |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Schindellegi, Switzerland | Freight Forwarding |
Agility Logistics | 1979 | Kuwait City, Kuwait | Freight Forwarding |
Bolloré Logistics | 1822 | Puteaux, France | Freight Forwarding |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany | Freight Forwarding |
YCH Group | 1955 | Singapore | Warehousing |
FM Global Logistics | 1988 | Selangor, Malaysia | Warehousing |
Century Logistics | 1970 | Shah Alam, Malaysia | Warehousing |
ICS Depot Services | 1997 | Selangor, Malaysia | Warehousing |
PKT Logistics Group | 1974 | Shah Alam, Malaysia | Warehousing |
Pos Malaysia | 1800s | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | CEP |
DHL Express | 1969 | Bonn, Germany | CEP |
GDEX (GD Express Carrier) | 1997 | Selangor, Malaysia | CEP |
Ninja Van | 2014 | Singapore | CEP |
J&T Express | 2015 | Jakarta, Indonesia | CEP |
FedEx Express | 1971 | Memphis, USA | CEP |
City-Link Express | 1979 | Selangor, Malaysia | CEP |
Aramex | 1982 | Dubai, UAE | CEP |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
GD Express: GD Express was in the process of parcel delivery and express logistics, having experienced a 10 percent increase from last year due to the constant strong demand nationwide for courier service deliveries from e-commerce products. In addition to its expanded network for delivery, it also made investment in automated sorting facilities that would boost internal efficiencies.
Pos Malaysia: Meanwhile, the national post office operator, Pos Malaysia, recorded a 15% year-on-year growth in its logistics segment this year with a higher last-mile delivery service and further penetration into rural markets. It said it is in discussions with several players in the e-commerce space for offering service development collaborations.
DHL Malaysia: Similarly, globally leading logistics player DHL Malaysia recorded a 12% rise in shipments amid growing demand from the manufacturing and automotive sectors, while DHL also expanded its cold chain logistics capability due to increasing demand for temperature-sensitive products.
Tiong Nam Logistics: With a very strong network in warehousing and distribution, the expansion of cold chain logistics serviced 7% of the revenue growth in 2023. Besides that, it invested in technologies to enhance supply chain visibility and operational efficiency.
FM Global Logistics: FM Global Logistics has greater interest in end-to-end logistics solutions and technological integration into logistics operations, therefore giving an 8% improvement in operational efficiency. In addition, the company is increasing its presence in Southeast Asia with a keen eye on the growth of cross-border logistics.
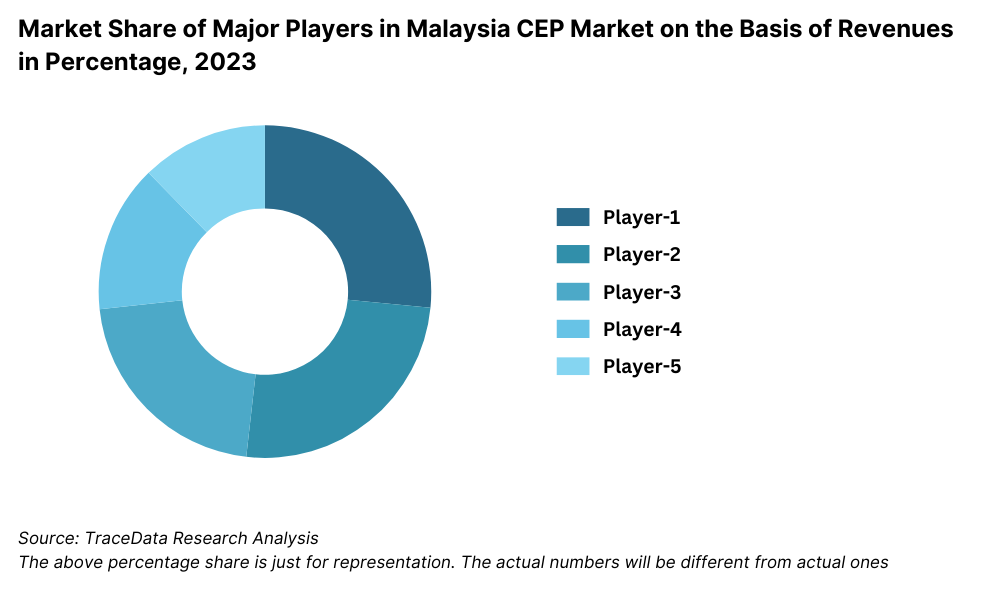
What Lies Ahead for Malaysia Logistics Market?
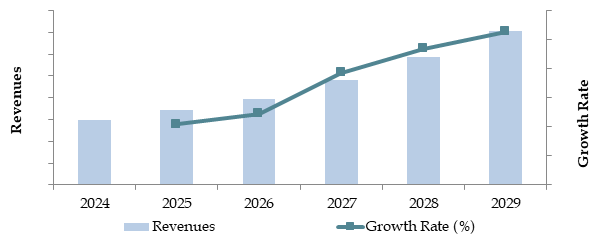
The Malaysia Logistics Market is expected to exhibit continued growth till 2029 with a decent CAGR during the forecasted period. Some of the factors that will drive growth include increasing trade activities, expanding e-commerce, and continuous investment by the government in developing infrastructure.
Adoption of Green Logistics: While there is growth in concern by the Malaysian government and its business towards the environment, green logistics can be considered to further develop in this field, entailing transportation using electric vehicles among other developments, as well as energy-efficient technologies being applied to warehouses. With incentive support provided by the government, 20% of logistics fleets by 2029 can include EVs that will contribute to reducing carbon emission from the sector.
Advanced technologies: The integration of AI, IoT, and big data analytics into operational methods in logistics, can change its very outlook and face. Technology will contribute to significant improvements that could enable better visibility of supply chain movements and route planning, while it will also enable an efficient and proactive approach toward effective management and handling inventory. More than 60% of companies in the logistics business will opt for Artificial Intelligence-infused solutions by the end of 2029, using which they are hoping to bring in an all-round increase of efficiency along with better economies for their customers as well.
Expansion of E-commerce Fulfillment Services: Headlong growth in e-commerce would further raise the demand for value-added logistics services, especially last-mile delivery and warehousing. E-commerce fulfillment markets are expected to grow at an 8% CAGR through 2029, with companies increasingly investing in automated warehousing solutions and real-time tracking systems to meet consumer expectations for fast and reliable deliveries.
Growth in Cold Chain Logistics: For the days ahead, cold chain logistics demand will get manifold, significantly by the two top industrial verticals pharmaceutical and food, which are poised towards vaccine distribution against the COVID-19 pandemic throughout the world; Malaysia's rising consumption of its cold chain commodities provides a very decent position for considerable growth. Given these factors, growth in the Cold Chain Market is expected in the segment around a range mark of 10% by the end of 2029, factoring in great demand for cold chain logistics service solutions.
Regional Development and Cross-Border Trade: Strategic location promotes regional trade, especially with its neighboring ASEAN countries. Further expanding regional free trade agreements and cross-border logistics corridors positions Malaysia to be strategically placed for logistics in Southeast Asia. The revenue share of cross-border logistics services is expected to account for around 25% of the total market revenue by 2029.
Future Outlook and Projections for Malaysia Logistics and Warehousing Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Malaysia Logistics Market Segmentation
Freight Forwarding Market
By Mode of Transportation
- Road Freight (Fleets, Volume, FTK, Price/ton/km and Revenue)
- Sea Freight (Fleets, Volume, Average Distance, Price/ton/km and Revenue)
- Air Freight (Volume, Average Distance, Price/ton/km and Revenue)
- By Road transportation
- Less than Truck load (Revenue and Volume)
- Full truck load (Revenue and Volume)
- By End Users (Revenues)
- Food & Beverages
- Textiles and Footwear
- Chemicals
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical consumables
- Electronics
- Others include agricultural products, frozen meat and more
Warehousing Market
By Business Model (Revenue, Price/sqm, warehousing space, Occupancy rate)
Industrial/Retail
CFS/ICD
Cold Storage
Agriculture
By Industrial warehouses (Revenues)
Grade A
Grade B
Grade C and others
By End Users (Revenues)
Food & Beverages
Textiles and Footwear
Chemicals
Pharmaceuticals and Medical consumables
Electronics
Others include agricultural products, frozen meat and more
CEP Market
By Channel
3PL Players
E-Commerce Merchants
By Type of Shipments
Domestic Shipments
International Shipments
By Area of Delivery
Intercity
Intracity
By Mode
Air Shipments
Ground Shipments
By Delivery Period
Same Day Delivery
1-2 Day Delivery
3-4 Day Delivery
More than 4 Day Delivery
By Type of Products
Consumer Electronics & Media
Fashion & Accessories
Foods & Personal Care
Home Care & Furniture
Toys & Baby Products
Others (Video Games, Digital Music, Pet Care, Home Gardening, etc.)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Kerry Logistics
- DHL Global Forwarding
- Tiong Nam Logistics
- Kuehne + Nagel
- Agility Logistics
- Bolloré Logistics
- DB Schenker
- YCH Group
- FM Global Logistics
- Century Logistics
- ICS Depot Services
- PKT Logistics Group
- Pos Malaysia
- DHL Express
- GDEX (GD Express Carrier)
- Ninja Van
- J&T Express
- FedEx Express
- City-Link Express
- Aramex
Key Target Audience:
Logistics Service Providers
E-commerce Companies
Manufacturers
Retail Chains
Pharmaceutical Companies
FMCG Companies
Government Regulatory Bodies
Investment Firms
Industry Associations
Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Macroeconomic framework for Malaysia Including GDP (2018-2024), GDP Growth (2018-2024), GDP Contribution by Sector
4.2. Logistics Sector Contribution to GDP and how the contribution has been changing in the historical assessment
4.3. Ease of Doing Business in Malaysia
4.4. LPI Index of Malaysia and Improvements in the last 10-15 Years
4.5. Custom Procedure and Custom Charges in Malaysia Logistics market
5.1. Landscape of Investment Parks and Free Trade Zones in Malaysia
5.2. Current Scenario for Logistics Infrastructure in Malaysia
5.3. Road Infrastructure in Malaysia including Road Network, Toll Charges and Toll Network, Major Goods Traded through Road, Major Flow Corridors for Road (Inbound and Outbound)
5.4. Air Infrastructure in Malaysia including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Air Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods traded through Air, Number of Commercial and passenger Airports, Air Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.5. Sea Infrastructure in Malaysia including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Sea Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Sea, Number of Ports for Coastal and Ocean Freight, Number of Vessels, Sea Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.6. Rail Infrastructure in Malaysia including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Rail Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Rail and others
6.1. Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2018-2024P
7.2. By End User Industries, 2018-2024P
8.1. Market Overview and Genesis
8.2. Malaysia Freight Forwarding Market Size by Revenues, 2018-2024P
8.3. Malaysia 3PL Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2018-2024P
8.3.1. By Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2018-2024P
8.3.1.1. Price per FTK for Road/Air/Sea and Rail in Malaysia
8.3.1.2. Road Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Number of Registered Vehicles)
8.3.1.3. Road Freight Domestic and International Corridors
8.3.1.4. Ocean Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity; Sea Ports Key Statistics)
8.3.1.5. Air Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue)
8.3.1.6. Rail Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity and Region)
8.3.1.7. Export-Import Scenario (Value by Mode of Transport, Commodity and Country; Volume by Principal Commodities)
8.3.2. By Intercity Road Freight Corridors, 2018-2024P
8.3.3. By International Road Freight Corridors (China, Thailand and India), 2018-2024P
8.3.4. By End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2018-2024P
8.4. Snapshot of Freight Truck Aggregators in Malaysia Including Company Overview, USP. Business Strategies, Future Plans, Business Model, Number of Fleets, Margins/Commission, Number of Booking, Major Clients, Average Booking Amount, Major Routes and others
8.5. Competitive Landscape in Malaysia Freight Forwarding Market, 2021
8.5.1. Heat Map of Major Players in Malaysia Freight Forwarding on the Basis of Service offering
8.5.2. Market Share of Maior Players in Malaysia Freight Forwarding Market, 2023
8.5.3. Cross Comparison of Major Players in Freight Forwarding Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Volume of Road Freight, Inception Year, Number of Fleets (Owned and Subcontracted), Fleets by Type, Occupancy Rate, Number of Employees, Major Route Network, Major Clients, Revenues, Volume of Sea Freight, Volume of Air Freight, USP, Business Strategy, Technology, (2023)
8.6. Malaysia Freight Forwarding Future Market Size by Revenues, 2025-2029
8.7. Malaysia Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2025-2029
8.7.1. Future Market Segmentation by Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2025-2029
8.7.2. Future Market Segmentation by International Road Freight Corridors (China, Thailand and India), 2025-2029
8.7.3. Future Market Segmentation by End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2025-2029
9.1. Market Overview and Genesis
9.2. Value Chain Analysis in Malaysia Warehousing Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
9.3. Malaysia Warehousing Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Warehousing Space, 2018-2024P
9.4. Malaysia Warehousing Market Segmentation
9.4.1. Malaysia Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2018-2024P
9.4.2. Malaysia Warehousing By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2018-2024P
9.4.3. Malaysia Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2018-2024P
9.4.4. 3PL Warehousing Space by Region, 2024P
9.5. Competitive Landscape in Malaysia Warehousing Market
9.5.1. Market share of Top 10 Companies in Malaysia Warehousing Market, 2023
9.5.2. Cross Comparison of Top 10 Warehousing Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Revenues from Warehousing, Number of Warehouses, Warehousing Space, Location of Warehouses, Type of Warehouses, Occupancy Rate, Rental Rates, Clients and others, (2023)
9.6. Malaysia Warehousing Future Market Size on the Basis of Revenues, 2025-2029
9.7. Malaysia Warehousing Market Future Segmentation
9.7.1. Malaysia Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2025-2029
9.7.2. Malaysia Warehousing Revenue By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2025-2029
9.7.3. Malaysia Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2025-2029
10.1. Market Overview and Genesis
10.2. Value Chain Analysis in Malaysia CEP Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
10.3. Revenue Composition and Contribution Between First Mile/Mid Mile and Last Mile Delivery-Analysis for Domestic and International Shipments
10.4. Malaysia CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2018-2024P
10.5. Malaysia CEP Market Segmentation, 2021
10.5.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2023-2024P
10.5.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2023-2024P
10.5.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2023-2024P
10.5.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2023-2024P
10.6. Competitive Landscape in Malaysia CEP Market, 2021
10.6.1. Overview and Genesis, Market Nature, Market Stage and Major Competing Parameters
10.6.2. Market Share of Companies in Malaysia CEP Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.3. Market Share of Top 5 Companies in Malaysia E-Commerce Shipment Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.4. Cross Comparison of Top 10 Malaysia CEP Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Number of last Mile Delivery Shipments, Revenues, Major Clients, Number of Fleets, Number of Employees, Number of Riders, Number of Pin Code Served, Major Service Offering and others
10.7. Malaysia CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2025-2029
10.8. Malaysia CEP Market Segmentation
10.8.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2025-2029
10.8.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2025-2029
10.8.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2025-2029
10.8.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2025-2029
11.1. Customer Cohort Analysis and End User Paradigm for Different Industry Verticals under Logistics Sector (Telecommunications, FMCG, Automotive, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.2. Understanding on Logistics Spend by End User, 2023-2024P
11.3. End User Preferences in terms of In-House or Outsourcing Logistics Services and Reason for Selection; Segregate this by Size of Company on the Basis of Revenues
11.4. Major Logistics Company who are Specialized in Serving Each Type of End User (Telecommunications, FMCG, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.5. Detailed Landscape of Each End Users across Parameters including Major Products Manufactured and Traded, Emerging Products, Type of Services Required, and Type of Services Outsourced, Major Companies, Contract Duration, Likelihood to Recommend, Market Orientation, Major Clusters, Type of Sourcing Preference, Pain Points, Facilities/Services Required, Future Outlook. Market Size for End User Industry Vertical with Growth Rate, 2018-2024P
12.1. Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
13. Malaysia Logistics and Warehousing Future Market Segmentation
13.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2025-2029
13.2. By End User Industries, 2025-2029
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Malaysia Logistics Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 logistics providers in the country based upon their financial information, market share, and service offerings.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the market size, revenue trends, number of market players, price levels, demand fluctuations, and technological advancements. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Malaysia Logistics Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue and service volumes for each player, thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential clients. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chain processes, service pricing, and other market factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis, along with market size modeling exercises, is undertaken to assess the sanity check process.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Malaysia Logistics Market?
The Malaysia logistics market is poised for substantial growth, with the market expected to reach a valuation of MYR 65 Billion by 2029. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing trade activities, the expansion of e-commerce, and continued investments in infrastructure. The market's potential is further enhanced by the adoption of advanced technologies and the strategic location of Malaysia as a logistics hub in Southeast Asia.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Malaysia Logistics Market?
The Malaysia Logistics Market features several key players, including GD Express, Pos Malaysia, and DHL Malaysia. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive distribution networks, advanced technology integration, and comprehensive service offfverings. Other notable players include Tiong Nam Logistics and FM Global Logistics.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Malaysia Logistics Market?
The primary growth drivers include Malaysia's strategic location along key shipping routes, the rapid expansion of the e-commerce sector, and government investments in infrastructure. Additionally, the increasing adoption of technology in logistics operations, such as AI and IoT, and the growing demand for cold chain logistics are expected to significantly contribute to the market's growth.
04 What are the Challenges in the Malaysia Logistics Market?
The Malaysia Logistics Market faces several challenges, including infrastructure bottlenecks, rising operational costs, and stringent regulatory requirements. Additionally, the market is challenged by a shortage of skilled labor and the need for more sustainable practices, particularly as global and local regulations increasingly focus on reducing carbon emissions within the logistics sector.